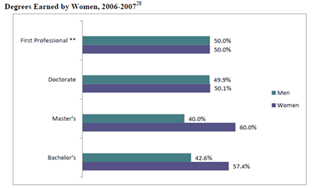
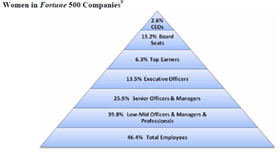
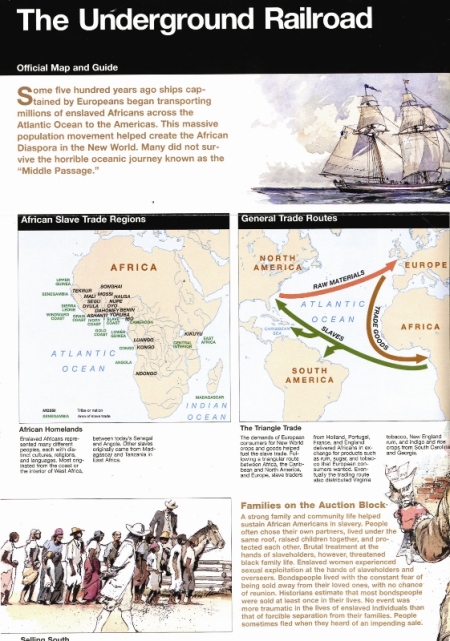
It’s that exciting time of year again if you’re a publisher of Federal publications. It’s the equivalent of the Academy Awards, the Emmy Awards or the Grammy Awards… Well, maybe that’s pushing it, but when the American Library Association’s (ALA) Government Documents Round Table or GODORT convenes the Notable Documents Panel of its Publications Committee to choose the top government-produced publications of the previous year, we can’t help but get caught up in the excitement.
It’s that exciting time of year again if you’re a publisher of Federal publications. It’s the equivalent of the Academy Awards, the Emmy Awards or the Grammy Awards… Well, maybe that’s pushing it, but when the American Library Association’s (ALA) Government Documents Round Table or GODORT convenes the Notable Documents Panel of its Publications Committee to choose the top government-produced publications of the previous year, we can’t help but get caught up in the excitement.
 Each year, this ALA GODORT Notable Documents Panel selects what it considers to be the most “Notable Government Documents” published during the previous year by Federal, state, and local governments and includes the list of winners in its prestigious Library Journal (LJ).
Each year, this ALA GODORT Notable Documents Panel selects what it considers to be the most “Notable Government Documents” published during the previous year by Federal, state, and local governments and includes the list of winners in its prestigious Library Journal (LJ).
According to its website, Library Journal is “the most trusted and respected publication for the library community. LJ provides groundbreaking features and analytical news reports covering technology, management, policy and other professional concerns to public, academic and institutional libraries. Its hefty reviews sections evaluate 8000+ reviews annually of books, ebooks, audiobooks, videos/DVDs, databases, systems and websites.“
This year, as usual, many of the Federal publications the panel selected are available through the Government Printing Office’s Federal Depository Library Program (FDLP) libraries and GPO’s Sales Program.
Out of all of the Federal Government documents LJ looked at in the past year, here are some of those it found most notable:
 |
Keeping America Informed: The United States Government Printing Office 150 Years of Service to the Nation
Publisher: Government Printing Office (GPO) GPO’s own role in producing excellent Government publications in its 150 years of history gained it a place on the GODORT list for the past year:“Liberally illustrated with historical photographs and facsimiles of famous government documents, this volume will appeal to a wider audience than depository librarians. Historians and history buffs who have an interest in government and how it interacts with both the private sector and public employee unions will find a compelling story that focuses on the federal government’s obligation to keep citizens informed about its activities.” – LJ |
 |
Statistical Abstract of the United States 2012 (Hardcover)
Statistical Abstract of the United States 2012 (Paperback) Publisher: Commerce Department, U.S. Census Bureau The Statistical Abstract of the United States, published since 1878, is the standard summary of statistics on the social, political, and economic organization of the United States. It is designed to serve as a convenient volume for statistical reference and as a guide to other statistical publications and sources. The latter function is served by the introductory text to each section, the source note appearing below each table, and Appendix I, which comprises the Guide to Sources of Statistics, the Guide to State Statistical Abstracts, and the Guide to Foreign Statistical Abstracts. The Library Journal adds an important update about this: “In addition to being the quintessential statistical resource of all time, Statistical Abstract is a Notable Document for 2011 simply because this edition will be the last produced by the Census Bureau and distributed through FDLP. Future editions will be published commercially, so librarians will still have options for maintaining the continuity of their print collections. A classic reference tool.” – LJ |
 |
Macondo: The Gulf Oil Disaster. Chief Counsel’s Report 2011
Publisher: National Commission on the BP Deepwater Horizon Oil Spill and Offshore Drilling “The National Commission on the BP Deepwater Horizon Oil Spill was created by President Obama and charged with investigating the root causes of the largest accidental marine oil spill in the history of the petroleum industry. The committee concluded that the cause of the blowout was not mechanical. Instead, a number of poor management decisions, combined with an inadequate regulatory structure and an indifferent regulatory agency, overwhelmed the safeguards designed to prevent such disasters. Plenty of illustrations and photographs offer a glimpse into the technology of offshore oil rigs.” – LJ |
 |
Then Came the Fire: Personal Accounts From the Pentagon, 11 September 2001
Publisher: Defense Dept., Army, Center of Military History “In 2011, there were many publications designed to commemorate the tenth anniversary of the attacks of September 11, 2001. In addition to the 59 people aboard the flight that struck the Pentagon, 125 people in the Pentagon were killed. The editors of this memorial volume have collected the stories of eyewitnesses, including the military and civilian personnel who escaped the burning building and first responders and reporters at the scene. It also includes hundreds of photographs.”- LJ |
 |
Freedom by the Sword: The U.S. Colored Troops, 1862-1867
Publisher: Defense Dept., Army, Center of Military History“ In what may be the definitive operational history of black troops in action during the Civil War, [author] Dobak describes the differences in how freedmen and runaway slaves were recruited, how they lived, and how they were trained. Most important, it considers how gallantly these men performed in combat at a time when many of their own leaders questioned whether they would be willing to fight for their own freedom and for that of their families. Much of the documentation comes from the ‘War of the Rebellion’ series.” – LJ |
 |
Legacy of Excellence: The Armed Forces Institute of Pathology 1862-2011
Publisher: Defense Dept., Army, US Army Medical Department Center and Schoo1, Armed Forces Institute of Pathology, Public Affairs Office, Borden Institute “In 1862, shortly after the Battle of Antietam, army surgeon general Brigadier Gen. William Hammond ordered the establishment of the Army Medical Museum. Surgeons working on Civil War battlefields were encouraged to preserve anatomical specimens, such as severed limbs and diseased organs, and send them to the museum for further research. From the start, the museum made its displays of specimens and instruments, as well as its medical library, available to the general public. Under the leadership of later curators, such as John Billings and Walter Reed, the museum evolved into the Armed Forces Institute of Pathology. Readers interested in the history of science, especially medical science or in the devastating effects of Civil War weaponry on the human body, will be fascinated by the hundreds of graphic photographs.” – LJ |
And a hearty congratulations to all the winning Federal agency publishers for an excellent job!
How can you get these publications from this year’s Federal Notable Government Documents collection?
- Buy any of these publications online 24/7 by shopping the Notable Government Documents 2012 collection at GPO’s Online Bookstore.
- Buy them at GPO’s retail bookstore at 710 North Capitol Street NW, Washington, DC 20401, open Monday-Friday, 9am to 4pm, except Federal holidays, (202) 512-0132.
- Find these publications in a library near you.
About the Author: Michele Bartram is Promotions Manager for GPO’s Publication and Information Sales Division and is responsible for online and offline marketing of the US Government Online Bookstore (http://bookstore.gpo.gov) and promoting Federal government content to the public.



 Posted by Michele Bartram, U.S. Government Online Bookstore
Posted by Michele Bartram, U.S. Government Online Bookstore